Ocean Acidification
Something in the Water
In a Flash
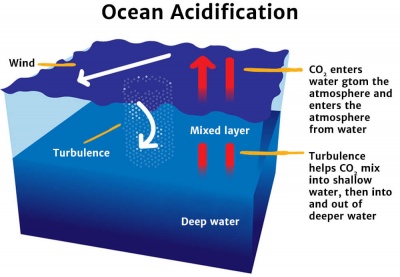
CO2 enters and mixes with shallow water and increases the ocean's acidity.
Acidification of the Ocean
Our oceans naturally absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When the ocean absorbs a lot of carbon dioxide, the water becomes more acidic.
Too much acidity can be seriously bad news for the ocean's ecosystems – and man-made climate change has caused ocean acidity to rise at alarming levels.
Burning Questions
What is ocean acidification?
Ocean acidification means our oceans are becoming more acidic. It is a change in the chemical make-up of the water resulting from too much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This change leads to a lowering of the pH level of the water.
How does carbon dioxide in the atmosphere affect the oceans?
Our oceans do a great job of 'sucking up' carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
But as carbon dioxide levels in the air have increased – due to things like burning fossil fuels – our oceans have taken in too much, leading to the water becoming much more acidic.

Changes in the ocean's chemical make-up threaten the health of coral reefs.
What impact does acidification have on ocean life?
Ocean acidification poses all sorts of threats to the rich ecosystems that exist in our oceans.
For example, it can make it difficult for sea creatures and coral reefs to make the strong shells they rely on for protection.
Ocean acidification can also make it harder for certain fish species to get around and find food.
Some examples of human activity impacting our oceans:

Dumping of industrial, nuclear, and other waste was legal until the early 1970s – but it still occurs illegally today.

Man-made pollutants that reach the ocean include pesticides, herbicides, chemical fertilizers, detergents, oil, sewage, and plastics.

Solid waste like bags, bottles, and other items dumped in the ocean are often consumed by marine mammals, fish, and birds – this can be fatal.

Oil spills cause huge damage to the marine environment.
How else does human activity affect the oceans?
Aside from acidification, our oceans have also suffered serious side-effects from human activities, such as over-fishing, pollution from run-off, and dumping of waste.
What Do You Mean?

Pollutants like industrial and plastic waste endanger the ocean's ecosystem.
Ocean acidification means a change in the chemical make-up of the water resulting in higher acidity.
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. A lower pH means higher acidity.
Speedy Summary
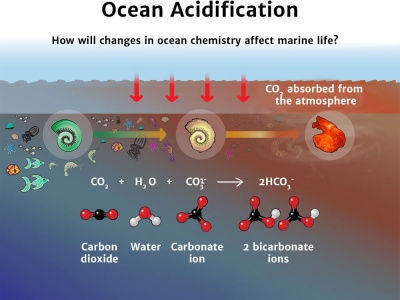
Excess CO2 increases the ocean's acidity, making it harder for some species to survive.
Ocean acidification means our oceans are becoming more acidic, due to the absorption of more carbon dioxide. Activities such as burning fossil fuels have contributed to the rising carbon dioxide levels in our atmosphere.
Teacher's Toolkit
Take this to the classroom!
Curriculum ready content.