Light Energy
Let it Shine
In a Flash

Sydney's Circular Quay bathed in visible electromagnetic radiation.
Light energy
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light consists of photons, which are produced when an object's atoms heat up. Light travels in waves and is the only form of energy visible to the human eye.
Burning Questions
What is light energy?
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength, which can be seen by the human eye. It is a type of kinetic energy.
How does light travel?
Light energy travels in the form of waves. Light energy is very fast – in fact, nothing travels faster.
How is light energy formed?
Light is made up of photons, which are like tiny packets of energy. When an object's atoms heat up, photon are produced from the movement of atoms. The hotter the object, the more photons are produced.
What are some examples of light energy?
Light energy is given off by things like stars, light bulbs, lasers, and hot objects.

Hot objects

Stars

Lightbulbs

Lasers
Our Sun – which is also a star – transmits light energy to Earth.
The Sun is a natural source of light energy.
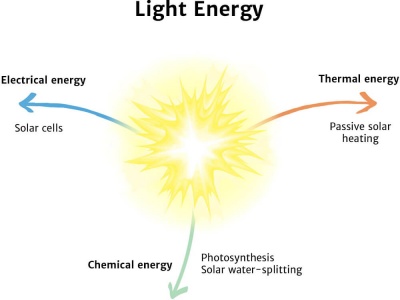
How is light energy used?
Light energy is used to help us see – either naturally using the Sun or fire, or with manmade objects like candles or lightbulbs.
Light energy is also used by plants, which capture the light energy from the Sun and use it to produce their food.
What Do You Mean?

The speed of light in a vacuum is 299,792 kilometres per second. Now that's fast!
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen by the human eye.
Photons are the particles that light is made up of, which are like tiny packets of energy.
The Sun is the closest star to the planet Earth and radiates light energy.
Speedy Summary

Glow Worms are capable for producing their own light. This process is called Bioluminescence.
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength, which can be seen by the human eye.
Teacher's Toolkit
Take this to the classroom!
Curriculum ready content.